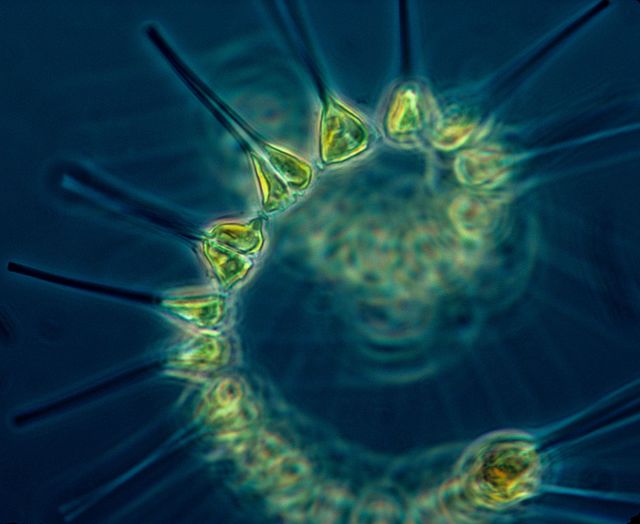
Informally called forams are single celled organisms members of a phylum or class of amoeboid protists characterized by streaming granular ectoplasm for catching food and other uses.
Phytoplankton shells deposited at the deep ocean floor.
Vast contributions of calcium carbonate deposits contributing to large sediments deposits in deep sea.
Siliceous ooze is a type of biogenic pelagic sediment located on the deep ocean floor siliceous oozes are the least common of the deep sea sediments and make up approximately 15 of the ocean floor.
Very small microscopic animals.
Introduction to ocean deposits 2.
Foraminifera f ə ˌ r æ m ə ˈ n ɪ f ə r ə.
If buried what type of rock will this sedimentary deposit most likely become.
Ocean floor and is eventually deposited.
Latin for hole bearers.
Pseudopodia entraps phytoplankton cells.
A river washes sediment into the ocean.
In this article we will discuss about 1.
The study of ocean marine deposits includes the consideration of types of sediments their.
Other deep sea sediments originate as skeleton remains of microscopic plants and tiny organisms.
This is the primary way in which sand is transported to the deep sea where the sediments are made up of tiny silt and clay particles.
They require a different form iron ii which more readily dissolves and is absorbed by cells.
Feeding method of foraminifera.
Most phytoplankton and other living organisms can t use iron in this state.
A diatom has cells made from silica.
Introduction to ocean deposits.
The sediment is composed of plankton and very fine particles of weathered silicate rock smaller than 0 05 mm in size.
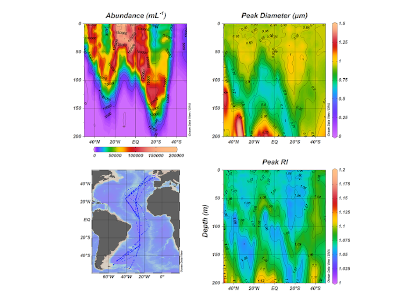
Deep ocean floors are covered by finer sediments than those of the continental margins and a greater proportion of deep sea sediment is of biogenous origin.
Thus the diatomite make the sand in the ocean healthier and have more density.
Hematite has another downside.
Sediments of the slope rise and deep ocean floor that originate in the ocean are called pelagic sediments.
Over billions of years layer upon layer fell to the sea floor forming iron ore deposits hundreds to thousands of feet deep.
Phytoplankton can only produce within a certain.
Classification of ocean deposits 3.
The material drifts down slowly through the deep quiet water and collects on the sea floor.
Another type from phytoplankton is a diatom.
Consists of 30 or more of the skeletal debris of microscopic organisms most of which live in water far above the deep sea floor within a few hundred meters of the ocean surface calcareous oozes composed mainly of the tiny shells of zooplankton.
These sediments are called biogenic sediments.
The unconsolidated sediments derived from various sources deposited at the sea floors are in cluded in ocean deposits.
Engulf entire phytoplankton cells and zooplankton of same size.
Observe ocean water temperature changes.
Siliceous oozes are largely composed of the silica based skeletons of microscopic marine.
Lives within or on substrate sea floor.